Lesson Notes
Notes from lessons
- Unit 3, Section 1.1: Data Types and Variables
- Add code in the space below
- The following is the code that adds the inputted addend to the other numbers. It is hidden from the user.
- lesson 3.3 and 3.4
- lesson plan for 3.5-3.7
- Unit 3 Sections 8 and 10 Notes!
- Unit 3 Sections 9 and 11
Unit 3, Section 1.1: Data Types and Variables
- variable is an abstraction that holds a value
- variables have meaningful names to help organize
- each different language has a specific way to store variables
- variables hold variable
- makes code more organized, variables can be compared to containers
- it is important to choose a name that correlates to the function
- integers for numbers
- strings stores text
- boolean true or false
- input function recieves input
- document.querySelector is a javascript code that you can use the query the code to find a certain class in order to find the button
3.2.2 Data Absraction with lists
- lists bundle together multiple elements under one name
- you can have different types of variables whithin one list
- the function list in python splits a string into a list of characters
- .join can join the characters together
Unit 3.1-3.3 Hacks
name = "alex" age = 16 print("name is", name) print("age is", age)In your own words, briefly explain by writing down what an assignment operator is
- an equal sign is an assignment operator as it assigns a variable to a value In Collegeboard pseudocode, what symbol is used to assign values to variables?
- the arrow is used to assign values A variable, x, is initially given a value of 15. Later on, the value for x is changed to 22. If you print x, would the command display 15 or 22?
- it would output 22
What is a list?
- a bundle of multiple elements What is an element
- an element could be a number or integer, string, or a boolean expression What is an easy way to reference the elements in a list or string?
- use index to find the elements in a list What is an example of a string?
- “amay” this is an example of a string
foods = ["pizza", "chicken", "steak", "pasta", "lasagna", "salad", "burger"] print(foods[3]) print(foods[-4])``` python num1=input(“Input a number. “) num2=input(“Input a number. “) num3=input(“Input a number. “) add=input(“How much would you like to add? “)
Add code in the space below
numlist = [num1,num2,num3]
The following is the code that adds the inputted addend to the other numbers. It is hidden from the user.
for i in [int(a) for a in numlist]: numlist[i -1] += int(add)
print(numlist)
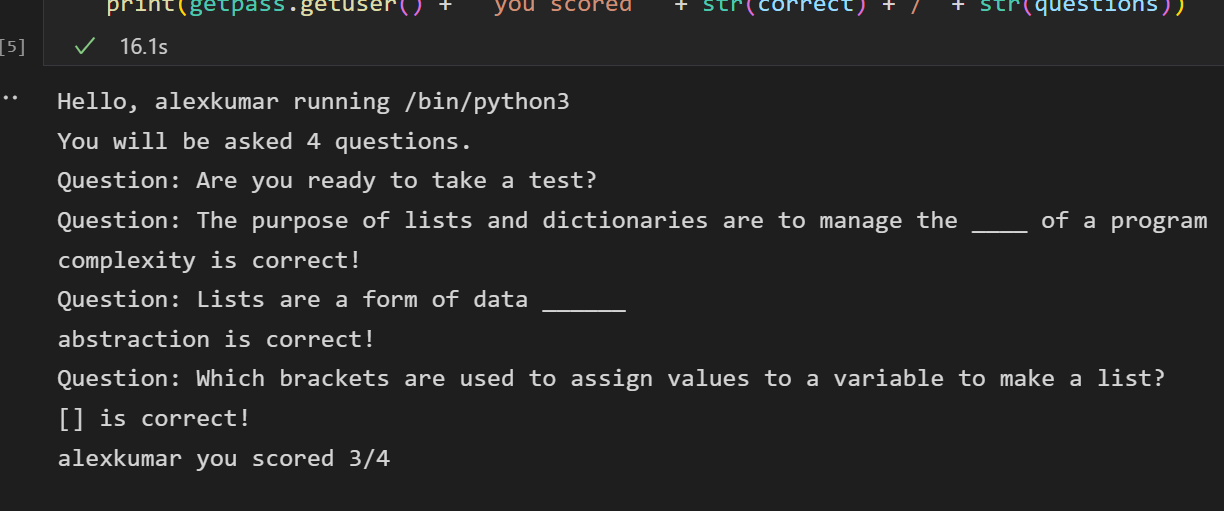
```python
foods = ["pizza", "hot dog", "sushi", "strawberry", "sandwhich"] #simplified foods list
# it is better to use lists because it is more simple
sports1 = "basketball"
sports2= "tennis"
sports3 = "soccer"
sports= ["basketball","tennis","soccer"]
lesson 3.3 and 3.4
- Algorithms are a finite set of instructions that can help you accomplish a task
- an algorithm is made up of sequencing selection and iteration
- A sequence is the orders or the instructions
- selection is what allows algorithms to make decisions
-
finally iteration is what repeats
- sequential statements specify how signals can be assigned
- sequencing is the order that the code explains these steps
- arithmetic operators, you can add and do basic operators by using + - / and *
- this operator % gives out the remainder
- len() gives the number of characters inside of a string
- concat(“”, “”) combines two different strings
- subtstring() can return specific characters of a string
HACKS for 3.3 and 3.4
- sequencing
- sequencing
- selection, sequencing
- iteration, sequencing
- sequencing
num1 = 5
num2 = num1 * 3
num3 = num2 / num1 * (9 % 2) * 4
result = (num3 % num1 + num2) % num3 * 3 / 5
this results in 3
hacks for 3.3
- iteration
- selection
- sequence
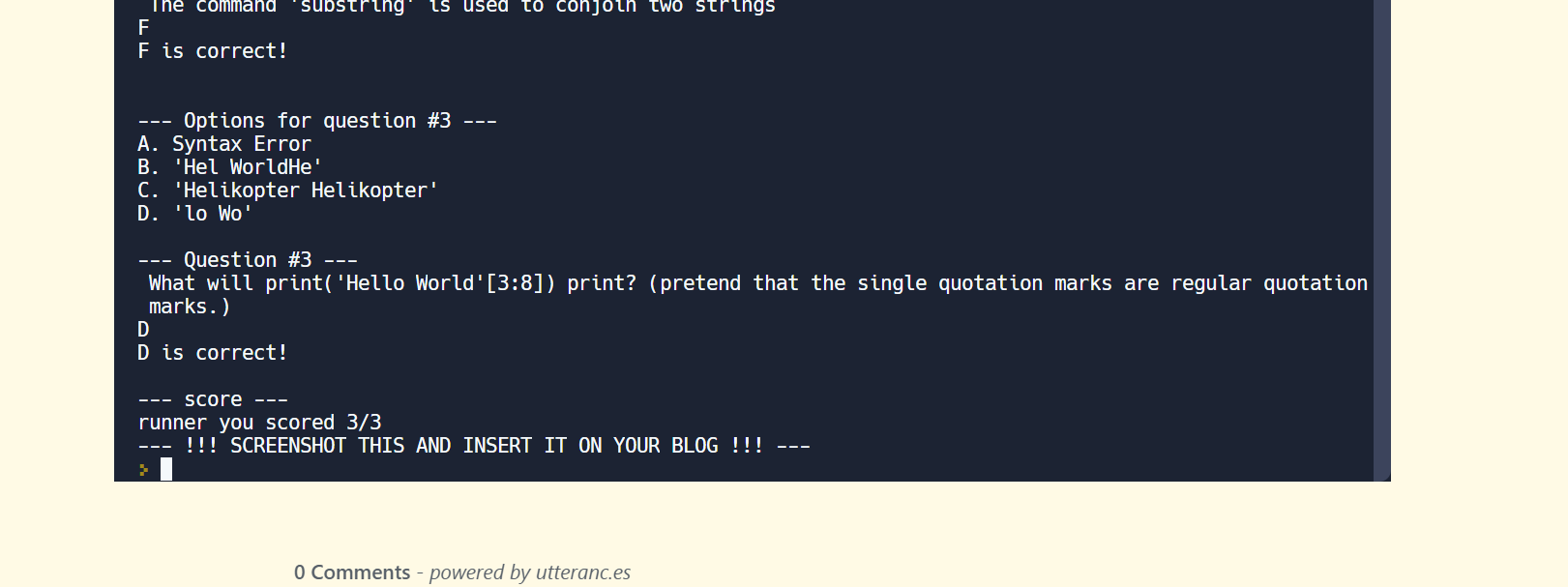
lesson plan for 3.5-3.7
- Conditionals allow us to check whether a function is true or false
- we can determine whether something is true or false based off of booleans
- True or False
- we can use binary to also check whether a condtional is true or false
- you can use elif statements to check for multiple different
- elif statements allow you to check for ideas such as whether an age is a certain level or a height is a certain height
- after these conditionals we can then output various things depending on the input
- to use binary for true or false, 1 represents true and 0 represents false
- 1 and 0 is 0
- 1 Xor 0 is 1
- 1 or 1 is 1
examples of if statements to check for basic conditionals
age = 0 cart = 0 # Put the code for ex:1 if age >= 16: print("works") # Put the code for ex:2 if cart < 4: ("works") - algorithms are a set of instructions that take in input and run a certain job and give an output
- selection uses conditionals to make a decision, for example like a boolean expression
Unit 3 Sections 8 and 10 Notes!
- 8.1
- Section Vocabulary:
Iteration: repeats a certain code blocks over and over as specified
Iteration Statements: repeats until a stopping condition is met
Repeat Until: repeats until blocks iterate over a certain code block until a certain condition is met, will not start unless the condition is false
- Break points can be used to check for conditions to stop looping
- It is very important to put break points so you don’t have to keep looping forever
- iteration is a repeating portion of a code
-
stopping conditions can be utilized in loops
- 3.8.2
- iteration statement: causes statements to be repeated
- when using range function, for example
for i in range(10) print(i) #or i = 0 while (i < 5): print("Hello, World!") i = i + 1 - These are both loops thata will iterate through the algorithm
3.8.3
sports = ["basketball","tennis"]
for i in sports:
if i == "basletball":
print(i)
- Another example of a for loop with embedded if statments
number = 0 while number < 10: if number % 2 == 0: print(number) number += 1 - this is a while loop that will checks if there is no remainer, if there is no remainder it will print otherwise it will just add 1
- This can be used to find even numbers and if you want to add them up you can also loop through an algorithm that will add the numbers together
- use int() to get numbers
Unit 3 Sections 9 and 11
- Algorithms can be written in different ways
print("What Grade Did You Get?") grade = int(input("Enter Grade:")) if grade >= 90: print("Wow! Good job!") if 70 <= grade < 90: print("Nice!") elif grade < 70: print("Do Better") - This code allows us to take an input of the grade and gives the output of a check of how they are doing
- small differences in code allows them to have different functions even if it is just the simple change in an operator
print("What Grade Did You Get?") grade = int(input("Enter Grade:")) A = grade >= 90 B = 70 <= grade < 90 C = grade < 70 if A: print("Wow! Good job!") elif B: print("Nice!") elif C: print("Do Better") - This is another function that does the same thing assigning a good job to an A grade
-
You can nest if statements to test for multiple conditions whithin a single if statement
- Creating outlines of a function before creating it allows you to develop it easier.
- Flowcharts are an easy way to visualize the algorithm
- Iteration can be used to cycle through an algorithm to check for a condition over and over again
- If the certain condition is not met it will keep repeating
- Binary search :repeatedly dividing a search interval in half
Unit 2… Binary/Data Terms
Bits: Bits are the individual numbers that describe binary Bytes, Hexadecimal / Nibbles Binary Numbers: Unsigned Integer, Signed Integer, Floating Point Binary Data Abstractions: Boolean, ASCII, Unicode, RGB Data Compression: Lossy, Lossless (note discussed yet) Unit 3… Algorithm/Programming Terms ——————- Variables: variables are storage
var = 3
This is an example of a variabe
Data Types: Some datatypes are string lists
list = []
This is a list
Assignment Operators: the arrow represents assignment operators
varknow = 6
we are assigning a value to this
Managing Complexity with Variables: Lists: lists can be used to store many types of data
sports = ["basketball","soccer"]
2D Lists,
list = []
Dictionaries: very good way to store keys and terms
dict = {"car":"good", "cat":,"bad"}
Class Algorithms, Algorithms help smplify code
def function():
print("hi")
def new():
print("this is a function"):
Sequence: represents the order
print("this is first")
print("this is after")
Selection makes decision based on data
if dog==True:
print("there is a dog")
Iteration this is aloop
for i in range(5):
print("hi")
this loops over 5 times
Expressions, Comparison Operators,some comparison terms are like < and >
if num1 > num2:
print("num1 is greater than num2")
Booleans Expressions and Selection, selects if a value is true or not
boolean = True
falseboolean = False
Booleans Expressions and Iteration, Truth Tables
function truth(){
var data = [[1,1], [1,0], [0,1], [0,0]];
var text = ""
for(let i =0; i < data.length; i++) {
text += data[i][0] + "&" + data[i][1] + "-->" + (data[i][0] & data[i][1]).toString() + "<br>"
}
for(let i =0; i < data.length; i++) {
text += data[i][0] + "|" + data[i][1] + "-->" + (data[i][0] | data[i][1]).toString() + "<br>"
}
for(let i =0; i < data.length; i++) {
text += data[i][0] + "^" + data[i][1] + "-->" + (data[i][0] ^ data[i][1]).toString() + "<br>"
}
let newdata = [1,0]
for(let i =0; i < newdata.length; i++) {
text += "~" + newdata[i] + "=" + ~newdata[i] + "<br>"
}
document.getElementById("text1").innerHTML = text
}
truth()
Characters,A word can be split into characters
word = "hi"
split = word.split()
Strings, basic values held in a variable
string = "hi"
Length, There is a length function that can get the length of any string
list = [1,2,3,4,5,6]
length = len(list)
This gets the length of the list
Concatenation, You can combine databases with this
import pandas
pd = pd.concat()
Python If, can check for certain conditions
if boolean=True:
print("any text here")
Elif, This can be used to check for a second function and this is very useful when choosing between certain conditions
if boolean=True:
print('good')
elif boolean=False:
print("this is bad")
Else conditionals;
if True:
print("this is true")
else:
print("not possible")
Nested Selection Statements
if True:
if dogs==True:
print("very good")
This can be used to checkfor many conditions whithin a certain condition, you can nest many conditions
Python For,
for i in range(5):
print(i)
While loops with Range,
while i<6:
i+= 1
Combining loops with conditionals to Break, Continue Procedural Abstraction, Python Def procedures, Parameters, Return Values